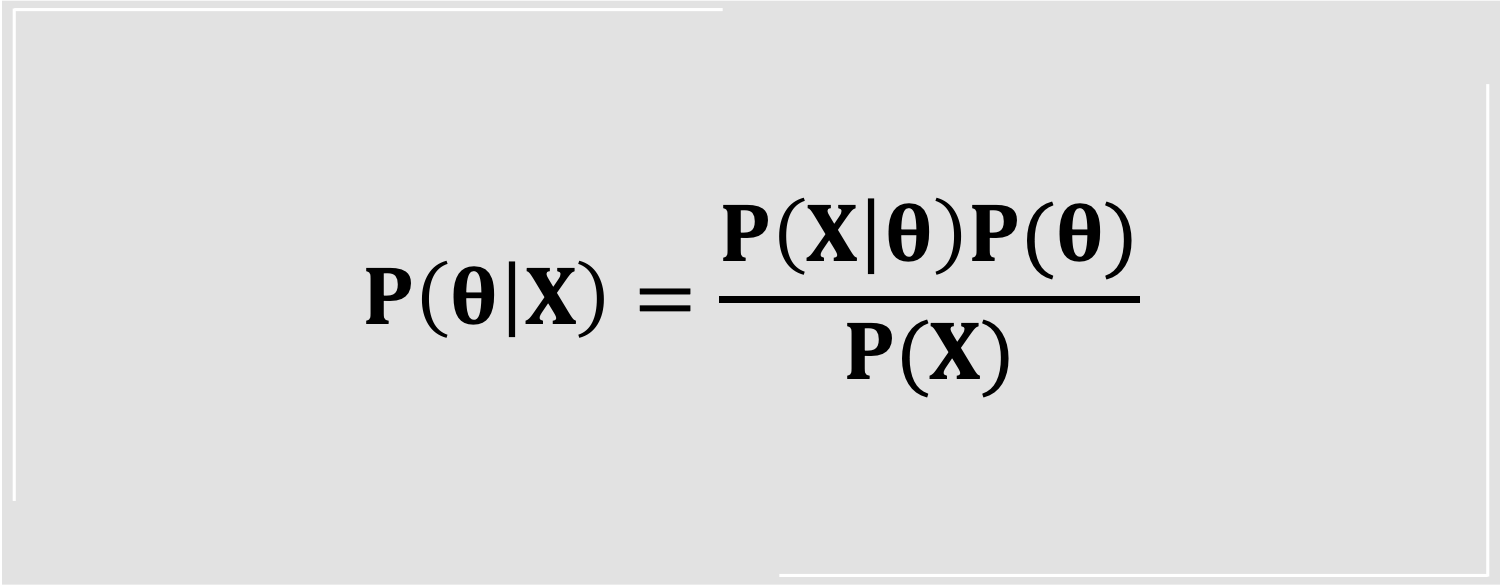
Knowledge is accumulated based on numbers and text. Each number represents the outcome of the observed event. Extract the information among numbers and estimated the randomness behind events are methods to gather knowledge. Based on probability, which describes randomness, Statistics is a collection of approaches that provides summaries and inferences. According to different utilizations on probability, two main schools are developed: Frequentist Statistics and Bayesian Statistics.
Before knowing the approaches deepen, we can start from an example in which we can apply Statistics. A scientific question is whether the average grades of senior high school students in Taiwan increasing by the year. The target is all Taiwan’s students; however, we can only obtain a small part of the record among them. As a result, we compute the average that represents the mean of all Taiwan’s students. The mean of all Taiwan’s students is the parameter that Statisticians are interested in this example. The way statisticians regard the parameter varies from the Frequentist Statistics and the Bayesian Statistics.
The most fundamental difference is inference, which includes the estimation of the parameter and its interval. Frequentist statisticians consider the parameter as a fixed number, while Bayesian statisticians believe the parameter is a random variable and from a distribution. Although the estimation of the parameter is the main goal in Statistics, the error of the estimation is also as important as the estimation. In Frequentist Statistics, Confidence Interval is proposed to measure the estimation error which uses the residuals and the size of the data (e.g. the number of the students in the above example). Whereas Bayesian statisticians create the Confidence Band that is from the corresponded distribution of the estimated parameter.
Despite the two schools are developed from the contrast concepts, the same results can be obtained sometimes. Bayesian Statistics result is affected by prior information specified. However, if no prior information could be used, the uniform distribution provides an informative prior distribution. Adopting uniform distribution leads to the same result as in Frequentist Statistics. For example, ridge regression is a well-known case.
Bayesian Statisticians and Frequentist Statisticians have not gotten along well with each other for a long time. The two schools are different roads, but they both concerned similar questions.